Oocyte and Embryo IVF Vitrification – Your Personal Golden Reserve
Vitrification is the most efficient and modern method of freezing eggs, embryos, and ovarian tissue for future use. Now IVF vitrification is a widespread fertility practice that helps women postpone pregnancy and have a baby at a mature age.

With age, the possibility of natural conception decreases, and the risks of miscarriage and chromosomal abnormalities in embryos increase. For example, a 32-year-old woman can produce 15-20 mature eggs with hormonal stimulation. Doctors can successfully fertilize 10-14 of them and get 4-8 embryos suitable for use. On the contrary, an average 40-year-old woman can only count on 4-15 mature oocytes, so at best, she can get three viable embryos, and at worst, none. It means that an entire IVF cycle of a 32-year-old woman has a 50% chance of success, and of a 42-year-old woman – only 20%.
After Kim Kardashian, Sofia Vergara, Nicole Kidman, and other celebrities officially announced that they would freeze their oocytes, the number of people who wanted to use this service has increased dramatically. That’s why in this article, we will highlight the history of egg and embryo IVF vitrification, find out if it is recommended for you, and tell you how it works. Let’s start with the method background.
History of Egg and Embryo Freezing and Cryopreservation
Japanese doctor Masashige Kuwayama is the father of IVF vitrification. He started his research in 1991, did experiments on cattle, and finally, 20 years later, invented the Cryotop vitrification method in 2000. Since then, it has been used over 500,000 times worldwide in over 1200 clinics in 40 countries with consistently excellent results. Dr. Kuwayama created the world’s first human oocyte (egg) bank and received the first vitrified embryo baby in Japan in 2002 and the USA in 2003.
Why Oocyte Vitrification Was so Hard to Invent?
Human oocytes and embryos mainly consist of water. As you know from physics, water crystalizes during freezing. Crystals break the egg structure and make it unable to survive. More issues arose when doctors needed to thaw eggs and embryos properly.
The main advantage of vitrification compared to the slow freezing method is no ice crystals form inside the egg. With slow freezing, only 50% of the embryos remained viable. However, 95 out of 100 embryos remain feasible after a freeze-thaw cycle with vitrification.
To Whom Is IVF Vitrification Recommended?
In addition to postponing motherhood for the future, vitrification helps women with fertility issues to become mothers. Here are some of the most often cases when fertility experts recommend women to opt for oocyte vitrification.
- Planned operations for benign tumors of the ovaries and uterus.
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer.
- Increased risk of OHSS (ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome) after superovulation in an IVF cycle. Embryologists freeze oocytes or embryos received via retrieval, save them until the woman fully recovers after the hormonal stimulation, and transplant embryos into the uterine cavity later.
- In all cases of reduced embryo implantation probability. Suppose there is an endometrial polyp, the insufficient thickness of the endometrium by the time of embryo transfer, or dysfunctional bleeding that can prevent embryos from implantation into the uterine cavity. In these cases, embryo vitrification can be helpful.
IVF Vitrification
In 50% of IVF protocols, women do not use all viable embryos for the transfer. They can use the remaining ones for cryopreservation and save them for later, or just in case. A cycle of freezing and transfer of thawed viable embryos will cost much less than a new IVF protocol.
In addition, many studies have found a higher rate of pregnancy and childbirth after the transfer of vitrified embryos compared to the transfer of fresh ones in a stimulated cycle. IVF with vitrification is better because women experience hormonal explosion during ovarian stimulation. When several follicles grow instead of one, it can negatively affect the endometrium and lead to early closure of the implantation window. Moreover, the pregnancy that occurs in a stimulated cycle is more often complicated by problems such as gestational diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, preeclampsia, and others. In the case of egg freezing, reproductologists can detect the best implantation time and postpone the transfer while the frozen embryos are safely waiting.
How is Egg Cryopreservation Performed?
Egg freezing implies the actual cryopreservation in the laboratory, the preparation, and the recovery stages.
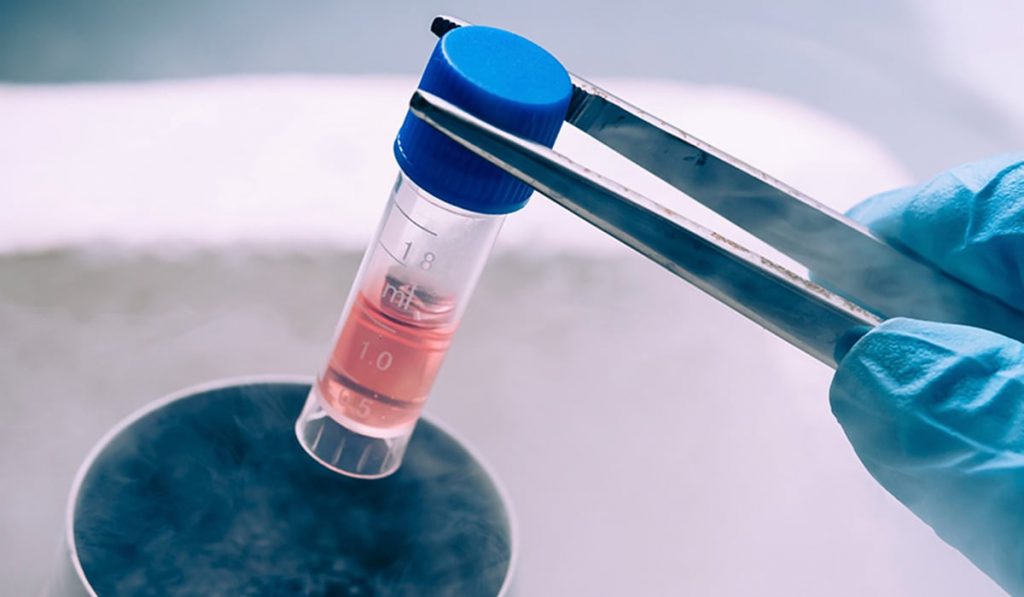
Follicle Puncture
Puncture is the collection of eggs from the ovarian follicles carried out in the operating room. During the procedure, the patient lies in a gynecological chair. The process takes place under general or local anesthesia. A reproductologist performs egg retrieval with ultrasound control using special catheters. The procedure takes about 15-20 minutes.
Cryopreservation Procedure
Immediately after collection, the follicular fluid goes to the embryologist, who scans it for the presence of oocytes. The more oocytes, the better. It is recommended to freeze at least 30 oocytes. Before cryopreservation, oocytes are sent for incubation, after which the mature eggs are frozen in the laboratory. The frozen material is sent to storage.
Rehabilitation of a Woman
After the procedure, a gynecologist and an anesthesiologist assess the woman’s condition. Usually, it is enough to lie down for 2 hours for rehabilitation to avoid complications after the procedure. Weakness and pulling pain in the lower abdomen are common consequences of egg collection for cryopreservation. A woman can return home the same day; she needs to avoid alcohol spicy food and decrease physical activity.
Vitrification of Donor Oocytes
Vitrification is very helpful in the case of donor IVF programs. If the intended parents choose an egg donor to obtain oocytes, there is no need to synchronize the cycles fully. One can use egg donor services, retrieve oocytes, vitrify them, or fertilize and freeze the embryos. It makes biological transportation possible. Embryos stay safely frozen even if you need to transport them to a different country.
Frequently Asked Questions about IVF Vitrification
If a woman, for some reason, has decided to preserve fertility, then there is only one recommendation from doctors – the sooner, the better! On average, the optimal age for maintaining fertility (vitrification of oocytes, embryos, ovarian tissue) is 30-35 years. But for each patient, this time is individual.
Vitrified oocytes can be stored for as long as desired. The main thing is to maintain optimal conditions for their storage. Most fertility clinics have cryobanks in big cities. Don’t hesitate to consult our experts if you want to know more about the nearest egg banks and clinics.
To vitrify oocytes, a woman must undergo a course of hormonal stimulation (about ten days of injections), at the end of which she will have a minor operation – ovarian puncture. Of course, she may experience some discomfort, but this does not affect her quality of life.
If a woman is somatically healthy, has no contraindications to pregnancy and childbirth, is ready to become a mother, this age can reach 45, 48, and even 50 years.